 What is Color Blindness?
What is Color Blindness?
Color blindness is a condition that affects the ability to distinguish between colors. It is a relatively common disorder, especially in males. The most common form is the inability to differentiate between red and green. In rare cases, individuals may be unable to distinguish any colors, seeing the world in black and white. Color blindness affects 1 in 20 men and 1 in 200 women. Many people do not realize they are colorblind until tested.
Causes of Color Blindness:
The exact cause of color blindness is not fully understood, but it is known to be a genetic condition. People with a family history of color blindness are more likely to be affected. In some cases, color blindness can develop due to neurological disorders. In hereditary color blindness, there is no loss of vision; it primarily affects color perception.
Symptoms of Color Blindness:
In hereditary color blindness, the most common type that typically develops from birth, green, yellow, orange, and red are perceived similarly, and these colors can only be distinguished by their intensity. Color blindness may not pose a significant problem in daily life but can affect the quality of life. People with color blindness may have difficulty performing certain tasks that require color differentiation.
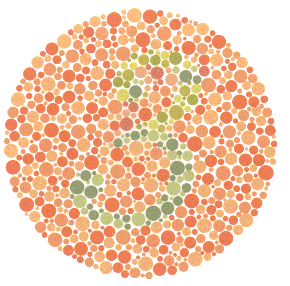
Color Blindness Test:
If you cannot read the numbers within the shapes shown, you may have color blindness. The human eye, through the iris, can perceive and distinguish colors. In cases of color perception issues in the retina, some or all colors may be perceived as grayscale. If you cannot distinguish numbers from surrounding colors in color blindness tests, it is highly probable that you have color blindness.
Treatment for Color Blindness:
 What is Chromagen?
What is Chromagen?
Chromagen is a unique product developed to assist individuals with color vision deficiencies and those struggling with reading difficulties. Chromagen haploscopic filters are specially colored and can be used as intraocular lenses or glasses. It has been observed to achieve a 97% success rate in trials, providing significant help to people with color blindness.
How Does Chromagen Work?
Chromagen Haploscopic lenses adjust the level of color perception for each eye, sometimes altering the perception for both dominant and non-dominant eyes, allowing better color distinction. For many people, the improvement in color perception and differentiation can be dramatic, with colors appearing brighter, richer, and more distinct, including those that were previously perceived incorrectly.
Uses of Chromagen Lenses:
- Enhance general color perception
- Ensure colors are seen more clearly and brightly
- Separate different color tones
- Identify colors
- Increase safety (e.g., recognizing traffic lights and warning signals)
- Improve performance in color vision tests
Chromagen lenses are not effective for patients who have color vision loss due to retinal or optic nerve disorders.